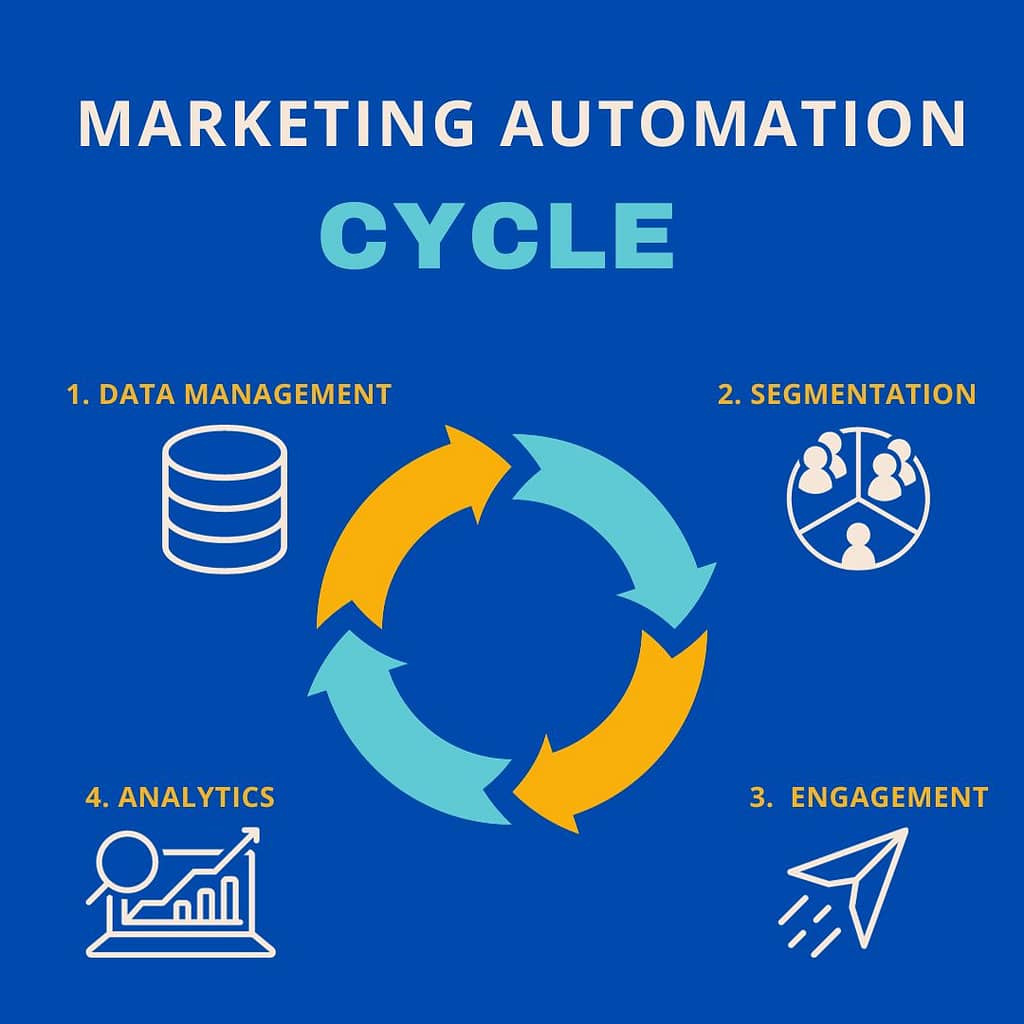
Marketing Automation cycle
Marketing automation is a technology-driven strategy that streamlines, automates, and measures marketing tasks and workflows. It aims to enhance efficiency, personalize customer experiences, and drive results by utilizing software platforms and technologies to automate repetitive tasks and nurture leads through the sales funnel.
Marketing automation is a multifaceted process comprised of four essential steps. First and foremost is data management, where the meticulous collection, cleansing, and integration of diverse data sources build a solid foundation.
Segmentation, the next step, involves dividing the audience based on demographics, behaviors, and interests, allowing for highly targeted and relevant campaigns.
The engagement phase follows, where personalized connections are established across channels like email, SMS, push notifications, and social media, fostering meaningful interactions.
Finally, analytics serve as the compass, offering insights into the impact of campaigns for continuous improvement. By navigating through these steps, marketing automation enables businesses to streamline processes, personalize experiences, and optimize outcomes.
1. Data Management: Building a Robust Foundation
Data Collection Strategies
Successful marketing automation begins with comprehensive data collection. Various touchpoints can be leveraged to gather valuable information about your audience.
Design user-friendly forms on your website or landing pages to capture essential details during sign-ups. Implement double opt-in tactics to enhance security and protect your forms from spam. Forms can serve various purposes, including surveys and product reviews.
Data Quality Assurance
Ensuring the integrity and accuracy of the data fueling your marketing automation is paramount for effective campaigns. A robust data quality assurance strategy involves steering clear of potential pitfalls. Avoiding spam traps, which are email addresses set up to identify and penalize spammers, is crucial for maintaining a positive sender reputation. Implementing double opt-in tactics not only enhances security but also ensures that your audience genuinely consents to receiving communications. Additionally, steering clear of cold lists—contacts who have not explicitly opted in—and regularly updating your database to exclude inactive or unengaged users contributes to a healthier and more responsive audience. By prioritizing data quality assurance, marketers can establish a foundation for successful and sustainable marketing automation campaigns.
Data integration
It is crucial to remember that a marketing platform should not undertake any data transformation, harmonization, or other resource-intensive processing activities. Another very important thing to remember is only to push data specifically intended for marketing purposes. By adhering to this principle, the marketing platform maintains a focused role, ensuring efficiency and optimal performance in delivering targeted and impactful marketing campaigns.
Now that we know what data loaded into our marketing platform should look like, let’s examine how we push data into the platform.
1. Flat Files and SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol): Old but Gold Standard
Old but gold, even in modern setups, this approach is still preferred for importing data. The use of flat files, such as CSV or Excel spreadsheets, for data exchange has been a long-standing practice. These files are then securely transferred using protocols like SFTP.
Advantages:
- Simplicity: Flat files are easy to create and understand.
- Compatibility: Almost every system supports file-based data exchange.
Considerations:
- Manual Process: Often involves manual handling and may not be suitable for real-time integration.
- Limited Scalability: May not be ideal for large-scale or frequent data transfers.
2. Built-in Connectors with CRM (Customer Relationship Management) Systems
Many marketing automation platforms come with built-in connectors for popular CRM systems like Salesforce, HubSpot, or Microsoft Dynamics.
Advantages:
- Seamless Integration: Streamlined connection with CRM systems for efficient data exchange.
Considerations:
- Platform Dependency: Compatibility depends on the specific marketing automation and CRM platforms.
- Real-time Updates: Allows for real-time updates between marketing automation and CRM platforms.
3. Custom Integration with Message Queues (e.g., SAP, Kafka, RabbitMQ)
Custom integrations involve connecting marketing automation platforms with enterprise-level message queues like SAP, Apache Kafka, or RabbitMQ. These queues facilitate communication between different systems.
Advantages:
- Scalability: Well-suited for handling large volumes of data and ensuring scalability.
- Real-time Processing: Enables real-time data processing and updates.
Considerations:
- Development Complexity: Custom integrations may require more development effort and expertise.
- Maintenance: Ongoing maintenance and updates are necessary to adapt to changes in systems.
The Importance of Data Cleansing
Regularly cleaning and updating your database is vital for accuracy and relevance. Remove duplicates, correct errors, and ensure that your data is up-to-date. This not only improves the effectiveness of your campaigns but also helps maintain a positive sender reputation.
Establish data retention rules to systematically clear the platform of unused data. Implementing clear and concise data retention policies not only ensures compliance with regulatory requirements but also enhances the platform’s efficiency by regularly removing unnecessary or outdated information.
2. Segmentation: Targeting the Right Audience
The Power of Segmentation
Segmentation is the cornerstone of personalized marketing. By categorizing your audience based on specific criteria, you can tailor messages to meet their unique needs and preferences.
- Demographic Segmentation: Grouping based on age, gender, location, and other demographic factors.
- Behavioral Segmentation: Categorization based on past interactions, such as website visits, email opens, and product purchases, is a common practice. Some tools, like Salesforce Marketing Cloud, offer in-house AI, EinsteinAI, that automates the preparation of certain behavioral segments for you.
- Psychographic Segmentation: Understanding audience interests, values, and lifestyle choices.
Targeted Messaging at the Right Time
Segmentation enables you to send targeted messages at the right time in the customer journey. Whether it’s a special promotion, product recommendation, or informational content, understanding your audience’s segment allows for more effective communication.
3. Engagement: Personalized Connections Across Channels
Understanding Engagement Strategies
Engagement in marketing automation goes beyond triggered sends; it involves creating personalized connections with your audience across multiple channels. The goal is to interact with your audience in meaningful ways, fostering relationships and driving desired actions.
Personalization Across Channels
Marketing automation enables businesses to engage with their audience on various channels, tailoring messages for a seamless and personalized experience:
- Email: Leverage personalized email campaigns to deliver targeted content based on user behaviors, preferences, and demographics.
- SMS (Short Message Service): Engage with your audience through concise and impactful text messages, offering promotions, updates, or important information.
- Push Notifications: Reach users on their mobile devices with personalized push notifications, keeping them informed and engaged with your brand.
- Social Media: Utilize automation to schedule and personalize social media posts, responding to audience interactions and fostering community engagement.
The Importance of Personalization
Personalization is at the heart of effective engagement in marketing automation. It involves tailoring your communication to individual preferences, behaviors, and characteristics. Key aspects of personalization include:
- Dynamic Content: Customize content based on user profiles, ensuring that each interaction is relevant and valuable.
- Behavioral Triggers: Respond to user actions in real-time, delivering personalized messages triggered by specific behaviors, such as website visits or product interactions.
- Segmentation: Divide your audience into segments based on demographics, interests, or past interactions, allowing for highly targeted and personalized campaigns.
Building Meaningful Connections
By engaging with your audience across various channels and incorporating personalization, you can build meaningful connections that go beyond one-time transactions. The ability to deliver the right message to the right person at the right time enhances customer satisfaction, loyalty, and long-term brand advocacy.
4. Data Analytics: Measuring Success and Iterating
Importance of Analytics in Marketing Automation
Analytics plays a pivotal role in assessing the success of your marketing automation efforts. Key metrics provide insights into user engagement, conversion rates, and overall campaign performance.
Key Metrics to Track in Email Marketing
- Open Rates: Measure how many recipients opened your emails, providing insights into the effectiveness of your subject lines and overall email appeal.
- Click-Through Rates (CTR): Track the number of users who clicked on links within your emails, indicating the level of interest and engagement with your content.
- Conversion Rates: Evaluate how many recipients completed the desired action, such as making a purchase or filling out a form. This metric directly ties into the effectiveness of your calls-to-action and campaign goals.
ROI Analysis
Analyzing the Return on Investment (ROI) of your campaigns is crucial for understanding the overall impact on your business objectives. Consider factors such as customer acquisition cost, lifetime value, and revenue generated from specific email marketing campaigns.
Continuous Improvement Through Analytics
Regularly analyze your email marketing metrics to identify patterns, trends, and areas for improvement. Use these insights to iterate on your strategies, adjusting content, timing, and targeting for optimal results.
What next?
Read our next blog to learn basic email marketing automation terminology.